Cross-Topic Integration (17 of 26)
Nonpolar substances such as lipids do not dissolve in water because their molecules in solution would prevent water molecules from forming as many hydrogen bonds as in pure water. This not only raises enthalpy in the water. It also imposes order on the water as it forms a kind of cage with dipoles directed laterally around a hydrophobic moeity. A polar substance such as a sugar is soluble in water because the decrease in the number of water-water bonds is compensated by the formulation of strong hydrogen bonds between the water molecules and the hydrogen bonds of the sugar so there is little increase in enthalpy.
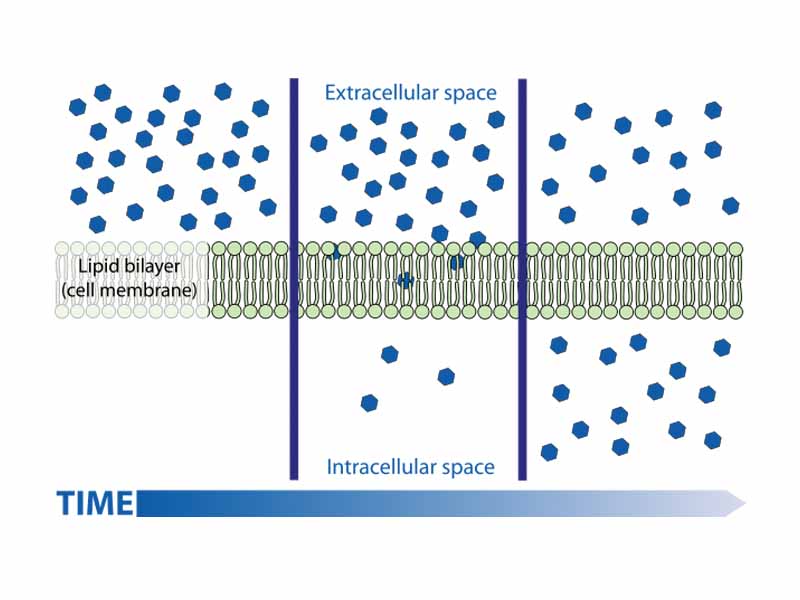
The solubility properties of a biological substance is one of its most important characteristics. For example, solubility determines which substances can pass directly through the nonpolar interior of the cell membrane (i.e. steroid hormones) and which substances require a channel (ions and sugars). Having a high partition coefficient into membrane lipids corresponds to a high diffusion rate through the membrane.