Cross-Topic Integration (18 of 26)
Henry's Law states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid is proportional to its partial pressure in the gaseous phase in contact with the liquid. This law helps to predict the amount of each gas which will go into solution. However, different gases have different solubilities which the solubility coefficient in the law takes into account.
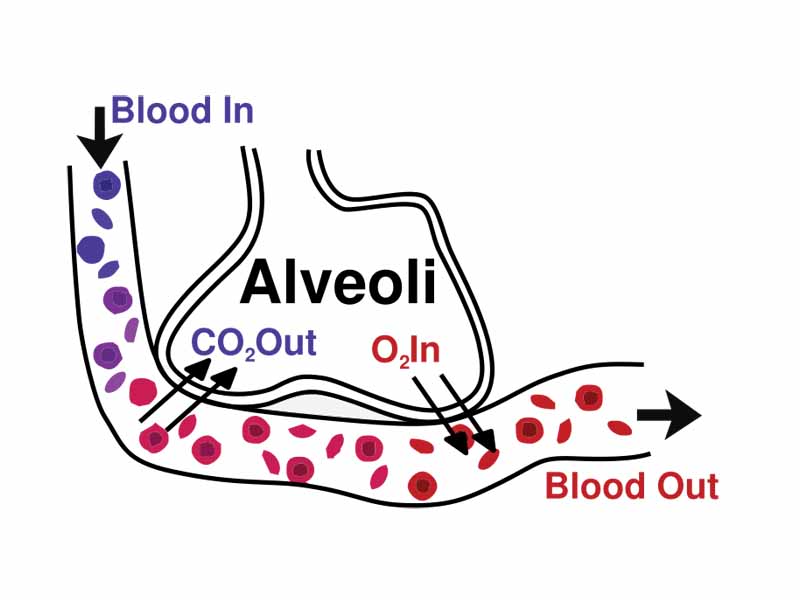
The MCAT loves straightforward questions on Henry's Law because it is one of those physical science principles directly applicable to medical education. Henry's Law is crucial to understanding gas exchange in the lungs, for example. Blood entering the lungs contains more carbon dioxide than would correspond to the Henry's Law equilibrium given the partial pressure of carbon dioxide in the alveoli, so carbon dioxide gas leaves the blood and enters the lungs. The opposite situation applies to oxygen gas. Oxygen leaves the alveolar air to enter the blood.